Understanding the NIST AI RMF Framework
The rapid advancement of artificial intelligence (AI) brings incredible opportunities, but also new and complex risks. From algorithmic bias to data privacy concerns, the potential for unintended harm is a significant challenge. To address this, the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) developed the AI Risk Management Framework (RMF). This voluntary framework provides a structured, proactive approach for organizations to manage the potential risks associated with AI systems throughout their lifecycle.
The creation of the NIST AI RMF was a collaborative effort, shaped by a congressional mandate from the National Artificial Intelligence Initiative Act of 2020. NIST led a multi-year process involving public workshops, requests for information, and several draft versions. This open, transparent, and collaborative approach allowed for input from hundreds of stakeholders across academia, industry, and government. The NIST AI RMF 1.0 was officially released on January 26, 2023, providing a crucial, consensus-driven resource to guide the responsible use of AI systems.
This framework isn’t a one-size-fits-all checklist. Instead, it’s designed to be a flexible resource that can be adapted to an organization’s specific needs, risk tolerance, and the unique characteristics of its AI systems. By focusing on a systematic process, it helps organizations build and implement innovative, trustworthy, and secure AI.
A Foundation for Effective AI Governance
At its core, the NIST AI RMF emphasizes a holistic approach to AI governance. This means embedding risk management practices directly into the development and deployment of AI technologies, rather than treating them as an afterthought. Effective AI governance involves:
- Clear accountability: Establishing clear roles, responsibilities, and accountability structures for every stage of an AI system’s lifecycle.
- Bias mitigation techniques: Using diverse datasets and continuous monitoring to reduce or eliminate harmful biases in AI models.
- Ethical compliance: Aligning AI practices with ethical standards and organizational values.
- Cybersecurity: Expanding upon existing cybersecurity principles to secure the AI data pipeline, protect model training environments, and defend against malicious attacks.
- Incident response plans: Having a plan in place to address and recover from unexpected or adverse AI behaviors.
NIST AI RMF Core Functions
The NIST AI RMF is built on four core functions that guide organizations in a continuous, iterative process for managing AI risk. These functions are meant to complement an organization’s existing risk management processes with guidance on how to effectively implement additional governance structures, risk assessments, and risk treatments in the context of AI.
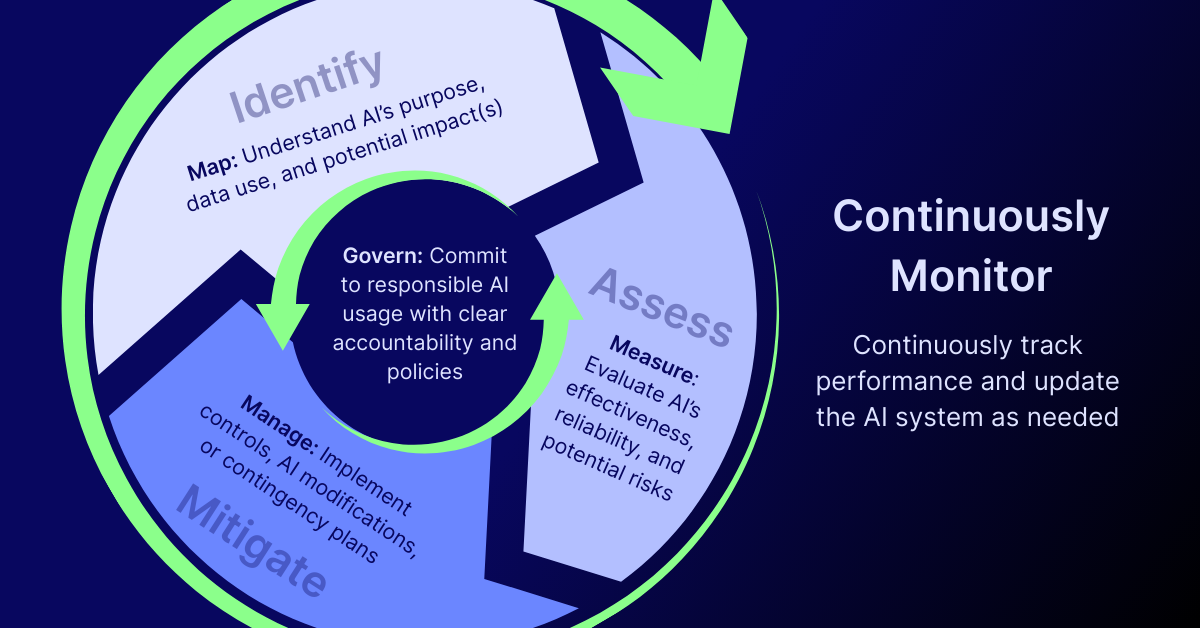
Govern
This function is all about creating a culture of risk management. It involves establishing the organizational structures, policies, and procedures needed to manage AI risks effectively. The Govern function ensures that leadership is committed to responsible AI and that clear lines of accountability are defined.
- Keep in mind: Unlike traditional IT, AI governance requires expertise that merges technical knowledge with ethical and societal awareness. Accountability for model outputs can be difficult to define, especially with complex models like generative AI and large language models.
- Actionable recommendation: Create a cross-functional AI Governance Committee to help ensure governance checkpoints are embedded throughout the AI development and implementation lifecycles.
Map
The Map function is about context and identification. It involves understanding the AI system’s purpose, the data it uses, and the potential impacts it could have on people, organizations, and society. This is where you identify vulnerabilities, potential harms, and any relevant legal or regulatory requirements.
- Keep in mind: Mapping AI risks is complex due to the dynamic nature of models and the potential for unintended consequences. Risks are often socio-technical, such as bias and lack of fairness, which are not traditionally covered by a cybersecurity framework. It requires mapping beyond technical threats to include social and ethical impacts in real-world contexts.
- Actionable Recommendation: Ensure your comprehensive inventory of AI systems maps back to core elements of GRC, like regulatory compliance and business continuity, for a holistic view of potential impact.
Measure
Once risks are mapped, the Measure function focuses on assessment. This involves utilizing quantitative and qualitative metrics to evaluate the effectiveness, reliability, and potential risks of an AI system. It includes assessing everything from performance and fairness to security and resilience.
- Keep in mind: Measuring AI requires evaluating more than technical risks, often including hard-to-quantify attributes like trustworthiness and fairness.
- Actionable recommendation: Create a unique risk assessment template that standardizes the qualitative and quantitative measurements of AI systems to ensure the socio-technical impacts on diverse business areas and groups of people are accounted for.
Manage
The Manage function is where you take action. Based on the insights from the Measure function, this involves prioritizing, treating, and mitigating identified risks. This can include implementing specific controls, modifying the AI system, or developing contingency plans to ensure the system remains compliant and secure.
- Keep in mind: Managing AI risks is an ongoing process that requires constant vigilance, often in real-time. It requires dynamic risk treatment for risks that evolve over time (e.g., emergent harms from a generative AI model) and for new threats like adversarial attacks.
- Actionable recommendation: Create an incident response plan tailored to AI-specific failures. Use automation and real-time monitoring to trigger alerts for emergent risks, and leverage platforms that provide a centralized view of all risks and mitigation efforts.
Is the NIST AI RMF Mandatory?
To be clear, the NIST AI RMF is a voluntary framework. It is not a regulation with mandatory compliance requirements or associated penalties for non-adherence. Instead, it serves as a guide for organizations to build trust and ensure the responsible development and use of AI.
However, many emerging regulations—such as the Colorado AI Act—explicitly reference the NIST AI RMF as an acceptable foundation for required risk programs. The benefits of implementing the framework are significant, as it helps organizations:
- Proactively manage risk: Identify and address potential issues before they cause harm.
- Build trust: Demonstrate a commitment to responsible and ethical AI to customers, partners, and the public.
- Align with evolving regulations: Prepare for future regulatory requirements by establishing a strong governance foundation.
- Improve decision-making: Use a risk-based approach to make more informed choices about AI development and deployment.
NIST AI RMF Implementation
The NIST AI RMF is designed for a broad range of AI actors, including AI developers, deployers, and end users. It’s relevant for anyone involved in the design, development, deployment, or use of AI systems, regardless of industry or size.
The framework can be applied across various AI use cases, from healthcare, where AI might assist in diagnosing diseases, to the supply chain, where it could optimize logistics. By providing a common language and set of practices, it helps diverse teams and stakeholders collaborate to build trustworthy AI systems that are reliable, secure, and fair.
How to implement the NIST AI RMF
Implementing any AI risk management framework, including the NIST AI RMF, is a strategic effort that is often broken down into three main stages: preparing for implementation, executing a tailored approach, and sustaining continuous improvement. Organizations can leverage several official NIST resources to guide their implementation:
- NIST AI RMF Playbook: This is a practical, companion guide to the framework that provides concrete steps and actionable suggestions for achieving the outcomes laid out in the AI RMF core. It offers a detailed list of sub-actions aligned with each of the four core functions, making the framework easier to operationalize.
- NIST AI RMF Roadmap: This resource outlines NIST’s long-term strategic plan for advancing the framework. It identifies key activities and areas for future development, providing organizations with a forward-looking perspective on how the framework will evolve. This helps organizations plan for future advancements and anticipate new guidance from NIST.
- The Generative AI Profile: This document is a companion to the framework specifically tailored for generative AI systems. It identifies unique risks posed by generative AI—such as model hallucinations, data poisoning, and the handling of sensitive data—and suggests actions for managing these risks.
What is the Difference between NIST AI RMF and ISO 42001?
While both the NIST AI RMF and ISO 42001 are foundational frameworks for managing AI risk, they have key differences in their approach and purpose.
ISO/IEC 42001 is an international standard for establishing, implementing, maintaining, and continually improving an AI management system (AIMS). It provides a more prescriptive, certifiable framework using a “plan-do-check-act” (PDCA), making it particularly valuable for companies operating globally or those that need to provide external proof of their AI governance.
The NIST AI RMF, on the other hand, is a more flexible, voluntary framework primarily used in the U.S. It focuses on providing a detailed, risk-based approach to AI governance that can be adapted to specific organizational contexts. It’s more of an internal playbook for building a robust risk management program rather than a standard for external certification. That being said, NIST has provided a cross-walk document between these two different frameworks.
| NIST AI RMF | ISO/IEC 42001 | |
| Summary | Flexible, internal playbook for AI risk management | Global, certifiable standard for AI governance |
| Target Audience | Primarily U.S.-based organizations, broad applicability | Globally recognized, ideal for those seeking certification |
| Methodology | Four core functions: Govern, Map, Measure, Manage | PDCA (Plan, Do, Check, Act) cycle |
| Compliance | Voluntary, but can be referenced to comply with regulations | Provides a path for external, third-party certification |
| Legal Context | Referenced in U.S. state laws like the Colorado AI Act | Referenced in international regulations like the EU AI Act |
An Integrated Approach to AI Risk
Implementing an AI risk management framework provides a crucial roadmap for organizations navigating the complexities of modern AI. By embracing the NIST AI RMF core principles—Govern, Map, Measure, and Manage—organizations can move beyond a reactive stance to a proactive and holistic approach. This integrated AI framework empowers teams to build trustworthy systems from the ground up, ensuring that technical and ethical considerations are intertwined at every stage. Implementing these safeguards not only helps to mitigate risks and ensure data protection, but also provides organizations with a competitive advantage by positioning them as innovative, responsible, and effective.
Conclusion: Your Roadmap to Trustworthy AI
Adopting a framework like the NIST AI RMF is not just a one-time project; it’s a roadmap for continuous improvement in AI security and governance. By engaging with the NIST AI RMF playbook and integrating its principles into your AI system lifecycle, you can proactively manage risks, foster innovation, and build a foundation of trust.This is where LogicGate’s AI Governance Solution becomes invaluable. It can help your organization operationalize the NIST AI RMF without starting from scratch—integrating with existing cyber and third-party risk management workflows to create a holistic view of technology risk, compliance posture, and operational impact. If you’re ready to help your organization safely keep pace with AI innovation, contact us today to schedule a personalized demo of Risk Cloud. We’ll show you exactly how our no-code platform can help you build a more connected, efficient, and resilient risk program.